Groundbreaking Discovery: NASA’s Perseverance Rover Finds Evidence of Ancient Microbial Life on Mars
Groundbreaking Discovery: NASA’s Perseverance Rover Finds Evidence of Ancient Microbial Life on Mars
On April 4, 2024, NASA’s Perseverance rover made a groundbreaking discovery that could potentially rewrite our understanding of life beyond Earth. The rover, which has been exploring the Jezero Crater on Mars since February 2021, has found compelling evidence of ancient microbial life on the Red Planet.
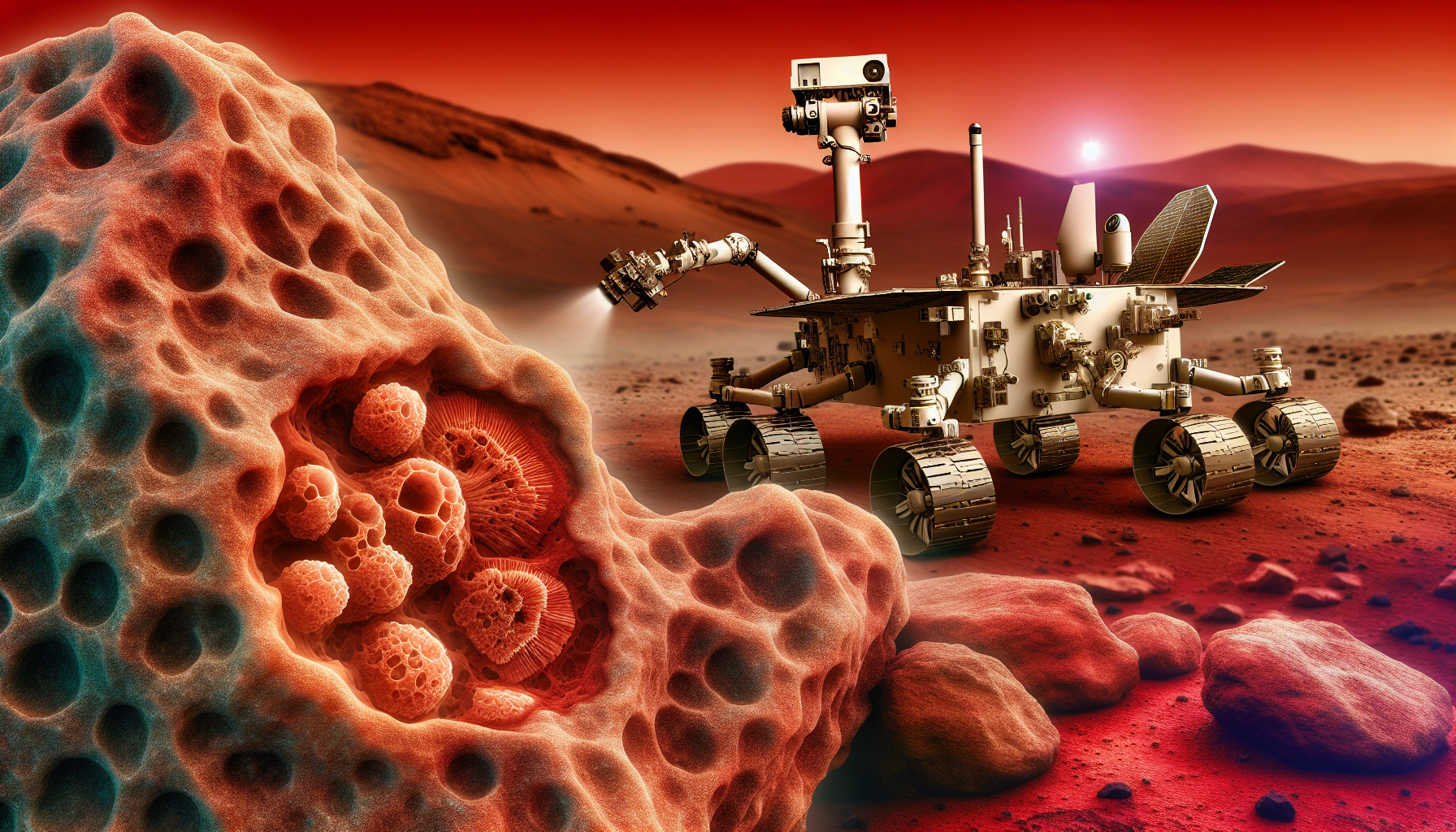 The discovery came as the rover was analyzing rock samples from the crater, which scientists believe was once a lake billions of years ago. The samples contained microscopic structures that closely resemble fossilized bacteria found on Earth. This discovery, if confirmed, would be the first direct evidence of past life on Mars.
The discovery came as the rover was analyzing rock samples from the crater, which scientists believe was once a lake billions of years ago. The samples contained microscopic structures that closely resemble fossilized bacteria found on Earth. This discovery, if confirmed, would be the first direct evidence of past life on Mars.
“This is a significant discovery,” said Dr. Jennifer Trosper, the project manager for the Perseverance mission at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. “While we have found indications of possible past water activity on Mars, this would be our first evidence of past life. It’s incredibly exciting.”
The rover’s instruments also detected organic molecules in the same rock samples, further supporting the possibility of past life. Organic molecules are the building blocks of life on Earth, but they can also be created in non-biological processes. However, their presence in the same samples as the potential microfossils is a promising sign.
While the findings are promising, scientists are proceeding with caution. “We have to be very careful in drawing conclusions from these observations,” said Dr. Trosper. “We are currently planning more experiments to confirm these results and to learn more about the possible biological origin of these structures.”
The Perseverance rover is part of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission, which aims to explore the possibility of past life on Mars, study the planet’s climate and geology, and collect samples for future return to Earth. This discovery marks a significant milestone in the mission and brings us one step closer to answering the age-old question: Are we alone in the universe?
Sources:
This information is based on the official press release from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the leading U.S. center for robotic exploration of the solar system. Additional information was obtained from the Mars 2020 mission website and the official NASA website.